Operators in C Language| Part-4
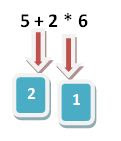
Unary operators Unary operator are those which only require one operand(argument) to operate. + , - , ++, --, typecast and sizeof are some unary operators in C programming. +5, -5 are the example of +,- unary operators. which represents +ve and -ve values. Unary operators have high priority than binary operators, so unary operators are always evalutes first. Increment / Decrement operator ++, -- are called increment and decrement operators. Increment and decrement operators are available in two versions Prefix Postfix Difference b/w prefix and postfix Prefix Postfix int a = 5; ++a; printf("%d",a); // 6 int a = 5; a++; printf("%d",a); // 6 int a = 5,b; b = ++a; printf("%d %d",a,b);// 6 6 int a = 5,b; b = a++; printf("%d %d",a,b);//6 5 Example of increment and decrement operators Example-1: int a = 3, b = 4,c; c = ++a * ++b; printf("%d %d %d",a,b,c); /...