Data types in Java
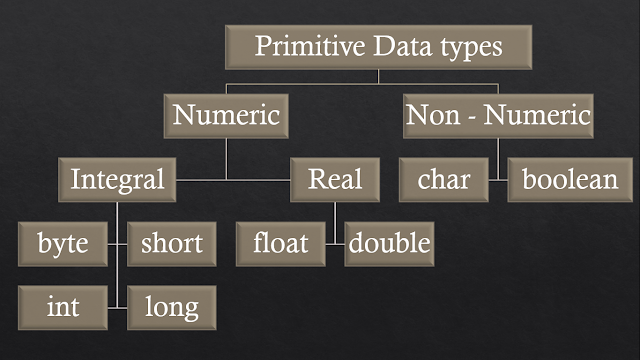
What is Data type In Java every variable have some type. For example in the code snippet below x should be int and b should be boolean type variable. x = 10; b = true; Similarly in Java every expression also have some type. For example in the following code snippet if a + b + c would result int type result because a, b and c are int type variables. int a, b, c, d; a = 1; b = 1; c = 1; d = a + b + c; Strictly type checking In Java, each type is strictly defined means byte have range from -128 to 127, so value out of from this range is not acceptable by byte type. Each assignment is strictly checked for type compatibility. Due to above two reason java is called strongly type checked language. Primitive Data Types 8 Primitive Data types in Java Signed / Unsigned Data types Examples int a = 10; ( ✓ ) int a = -10; ( ✓ ) float x = -5.8; ( ✓ ) char ch = -'a'; (✕) boolean b = -true; (✕) bool...